Import
Learn Importer's Language
International Trade Terms
The following shipping terms are essentially factual but not complete in its full context. For terminology which is not fully understood or cannot be found in this section, we would suggest you to refer your query to your freight forwarder or export adviser.
Alternatively, you may want to consult the enquiry desk of MATRADE (Malaysia ExternalTrade Development Corporation).
Ad Valorem |
Latin word which means according to value. Customs duties and taxes are calculated on the basis of value. In other words, ad valorem tariff is calculated according to value or as a percentage of the value of goods. |
|---|---|
Advising Bank |
A bank that notifies or advises the exporter that a credit has been opened in the exporter's favour. The advising bank, usually located in the exporter's country, informs the exporter of the conditions of the documentary credit without itself making a payment commitment. |
Agent |
A person or an entity authorized to undertake a business transaction for and on behalf of another person or entity. Different names lik a broker, commission agent, sales agent, manufacturer's representative, buyer's agent are used but essentially they acted in the same capacity, i.e. acting for and on behalf of another party. |
All Risk Insurance |
A type of insurance coverage that excludes only the risks that have been specifically outlined in the contract, otherwise it means that any risk that is not specifically omitted is automatically covered. In short, it is the broadest form of coverage for any loss of or damage to the cargo during the transit. It should be noted that coverage on War, Strikes, Riots and Civil Commotion (W&SRCC) is also always excluded in all forms of insurance coverage unless separately and specifically covered. This term is now being phased out and the new term "Institute Cargo Clause (All Risks)" is now being used instead. |
Anti-Dumping Duty |
Duty imposed to offset the amount or margin of dumping. The introduction of this duty is to protect the domestic market from being made use of by certain foreign manufacturers in disposing their products, thereby destroying the pricing mechanism of that certain products. |
Arbitration |
A process of dispute resolution 1n which a neμtr_§) third party (arbitrator) renders a decision after a hearing at which both parties have an opportunity to be heard. Arbitration may be voluntary or contractually specified ·n writing. The advantages of arbitration, as compared to litigation, are neutrality, confidentiality, reduced costs, faster procedures and the arbitrator's expertise in specific areas. Internationally, the main arbitration body is the International Chamber of Commerce; other arbitration institutions include the London Court of International Arbitration. Malaysia has an arbitration center - Kuala Lumpur Regional Center for Arbitration. |
Assignment |
A term commonly used in connection with a transport document, more frequently with Bill of Lading. it involves the transferring of rights, title and interest in order to assign goods by the endorsing the Bill of Lading or any other transport document. |
ATA Camet |
'Admission Temporal/Temporary Admission'. An international customs document for the temporary duty-free admission of goods into a country for display, demonstration or similar purposes. ATA Carnets are issued by National Chambers of Commerce, which guarantee the payment of duties to local customs authorities should the goods allowed In are not be ultimately re-exported. |
Bill of Exchange |
A negotiable instrument that represents an unconditional demand for payment. Together with B/L it forms the basis for documentary collection procedures and together with exporter's commercial invoice it can be used to demand payment from importer for the goods. Definition from Bill of Exchange Act states: "An unconditional order in writing, addressed by one person to another, signed by the person giving it requiring the person to whom it is addressed to pay on demand, or at a fixed or determinable future time, a sum certain in money to or to the order of a specified person, or to a bearer'. A bill is signed by a drawer acid addressed to a drawee, who becomes the acceptor by writing their name across the face of the bill. The person to whom the bill is payable is referred to as the payee. |
Bond |
An undertaking, usually in legal format, by a person or entity who binds himself to the authorities (more frequently the Customs) to conduct his commercial transaction or the act of doing so, as specified by the law, regulations or conditions. Sometimes, referred to as Customs Bond. |
Bonded Goods |
Imported goods that are stored in a bonded warehouse, usually after the owners of the goods have not found a buyer for the goods yet and would withdraw the goods after finding a buyer or reexported out to another country. Should the goods be sold to a domestic buyer, the owner of the goods would pay the appropriate duty/tax, unless the buyer has already obtained an exemption from the customs authority. |
CAD (Cash against Document) |
A payment at sight of documents presented. When an indicated invoice amount to be paid by the 0uyer I importer at sight on commercial documents (e.g. bill of lading, insurance certificate, etc.). |
Carriage Paid To (CPT) |
See lncoterms. |
Carriage and Insurance Paid To ... (CIP) |
See lncoterms. |
CBD (Cash before delivery) |
A payment before a delivery takes place. Rather simffar to COD, except that delivery is usually not effected until payment is received. |
Certificate of Health |
A certificate of health or health inspection certificate may be required by an overseas buyer or by the authorities in the buyer's country. Usually, an official health certificate issued by the export-side health authority states that the animal exported out of the country is healthy, free from signs of infectious or contagious diseases and signs of internal and/or external parasites, and meets the specific requirements staled in the regulations of the exporting country. |
Certificate of Insurance |
A document issued by an insurance underwriter to the exporter (or the freight forwarder) to provide evidence that insurance against loss or damage of the goods to be exported has been obtained. A "Certificate of Insurance" has no legal standing and usually banks insist on obtaining the Insurance policy, in which case is a legal document. |
Certificate of Origin |
A document Issued by a competent authority that certifies the country where the product was made in. A Certificate of Origin is sometimes required by the importing country's authorities to prove that the goods originate from a particular country. This may be necessary to enable an Importer to claim preferential Import duty, in which case, it is known as "Preferential Certificate of Origin (PCO)". A competent authority may be the National Chamber of Commerce or Department of Trade or Industry. In case of Malaysia, PCO is issued by Ministry of International Trade and Industry, whilst normal Certificate of Origin is issued by the respective Chambers of Commerce (like ACCCIM, MICCI or FMM). |
Certificate of Shipment |
A document issued by the shipper I supplier I intermediary-to certify the state of conditions of the goods prior to delivery or shipment. In order to verify to the receiver I consignee I other intermediaries (like bank or customs authority) that the stipulated conditions are complied with. Maybe used by a different party in a differing situation, including certifying different parts of a journey covered under a through BIL, certi_fying cargo shipped for storage at an intermediate location/warehouse, etc. |
CKD (Completely Knocked Down) |
Abbreviation for "Completely Knocked Down". Different parts and components are shipped to one plant for assembly into a final product. |
Clearance for Home Use |
See lncoterms. |
Carriage and Insurance Paid To ... (CIP) |
Goods are imported where Customs authority approves the importation for free circulation in a country, upon compliance of all regulations and payment of duties and taxes, to any. |
COD (Cash on Delivery) |
A payment at a point of delivery. Where small value goods are sent by post I courier and are released only after payment of the invoice plus any COD charges, if levied. |
Consular Invoice |
An invoice covering a shipment of goods certified (legalized) by the consul of the country for which the goods are destined. The invoice is used by customs officials of the country to verify the value, quantity and nature of the goods Imported for the computation of import duty. In addition, the export price may be examined by the consul to ensure that dumping is not taking place. |
Commercial Invoice |
A document containing commercial transaction between a seller (exporter} and a buyer (importer), comprising of information such as a complete listing and description of the goods including prices, discounts and quantities, and the delivery and payment terms. A commercial invoice is generally used by customs to determine the true value of goods for the assessment of customs duties and must therefore, conform to the regulations of the importing country. See more in 3.2 International Shipping Terms. |
Confirming Bank |
In documentary credit transactions, the bank which adds its own irrevocable undertaking for payment in addition to that given by the issuing bank. The confirming bank is usually located in the exporter's country. See also Documentary Credit |
Common External Tariff (CET or CXT) |
A common tariff uniformly applied by a common market or customs union (such as EU, Mercosur) for imports from ceuntries outside the group or union. This is to prevent the re-exportation from one member country to another, this unifying the tariff . |
Cost and Freight (CFR or C&F) |
See lncoterms. |
Cost, Insurance and Freight (CIF) |
See lncoterms. |
CMR Note |
A consignment note with a standard set of transport and liability conditions, as provided under CMR convention. Unlike the BIL, a CMR note is not a document of title but merely a receipt of goods by the road carrier and a contract of carriage existed between the carrier and the trader. |
CMR Convention |
Abbreviation for "Convention relative au contrat de transport international de marchandises par route" (in French) which translates as "Convention on the Contract for the International Carriage of Goods by Road". The CMR Convenjion is an international convention that was signed on 19 May 1956. It relates to various legal issues concerning transportation of cargo by road. |
Cover Note |
A simplified set of document, usually issued by an insurance writer or broker to the exporter, confirming the status ot insurance coverage on the goods as declared therein. |
Copyright |
An exclusive right granted by a government authority for a spectfied period to the creator of literary or works of art, such as books, articles, drawings, charts, musical lyrics, recordings, motion pictures and computer programs. |
CIM Convention |
CIM Convention Abbreviation for "Convention Internationale concernant le transport des Marchandises par chemln de fer" (In French) which translates as "International Convention concerning the Carriage of Goods by Rail". This convention is evolved to be Appendix B to the later convention COTIF. |
CRN (Customs Registered Number) |
A unique identification code which identifies an Exporter or Importer approved to use certain customs procedures. |
INCOTERMS
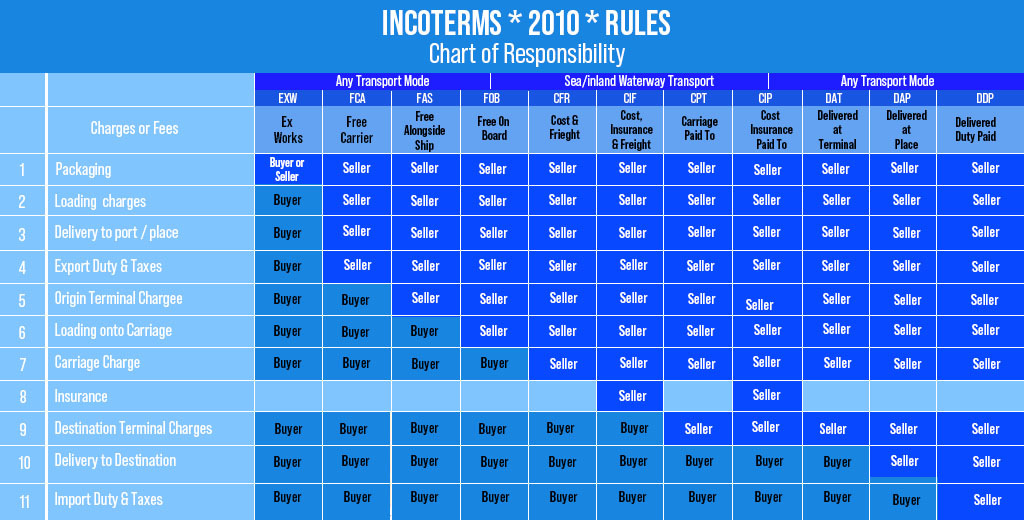
International Shipping Terms
The following shipping terms are essentially factual but not complete in its full context. For terminology which is not fully understood or cannot be found in this section, we would suggest you to refer your query to your freight forwarder or export adviser.
Alternatively, you may want to consult the enquiry desk of MATRADE (Malaysia External Trade Development Corporation).
ATA |
Actual Time of Arrival of the vessel at the port. |
|---|---|
ATD |
Actual Time of Departure of the vessel from the port. |
Air Freight |
Usually Air Freight is charged at the same rate irrespective of the class of goods. These may be charged in one of the three ways, namely by weight. by volume or by value (ad valorem) and normal air freight quotation covers airport to airport only. |
AirWay Bill (AWB) |
A document which evidences a contract of carriage of goods by air between a shipper and an air carrier. Technically, an AWB is not a, negotiable instrument but however serves as a receipt for the shipper, indicating that the carrier has accepted the goods listed therein and obligates to carry the consignment to the airport of destination in accordance with the specified conditions printed therein. AWB issued by the air carrier (airline) Is normally referred to as Master Air Waybill (MAWB) carrying the reference numbers, starting with three numeric digits of airline identification codes issued by IATA to non-US based airlines and Air Transport Association of America (A4A) to US-based airlines. The next 7 digits are running numbers and the 8th digit is a "check-digit' which serves to double check the accuracy of the 7 running numbers. In addition, air freight forwarders also issue HAWB (House Air Waybill) to their customers for each of the shipments. |
Arrival Notice |
An advice that a carrier or forwarder sends to the consignee advising of goods coming forward for delivery. Only essential information such as Bill of Lading number, container number and total charges due from the consignee are only included in the advice and sent to the consignee prior to vessel's arrival. This is done by the carrier or forwarder to ensure smooth delivery. However, the responsibility to monitor the vessel transit time and presenting him settto take timely delivery still rests with the consignee or his appointed servant. |
Automated Manifest System (AMS) |
An application that expedites the clearance of cargo for the subsequent release of containers when imported into U.S.A. through the electronic submission of cargo manifests, 24 hours before loading at the origin port. |
Back Haul |
A term used to indicate the backward (reverse) portion of the forward route which a carrier has performed. The return cargo, usually in the opposite direction, is the back-haul freight. |
Bill of lading (BIL) |
A document issued by an ocean carrier to a consignor (the shipper of the goods) which serves as (1) a receipt for the goods delivered to the carrier for shipment, (2) an expressed definition of the contract of carriage of the goods and (3} a document of title to the goods described therein. A B/L is generally "not negotiable" unless it is made "To Order" in the consignee column. Fundamentally, B/L is a contract between the owner of the goods and the carrier. One form of BIL is called the "straight BIL" which is non-negotiable, as it is consigned directly to a designated party named therein. A "negotiable B/L" can be bought, sold, or traded while goods are in transit is capable of transferring title of goods covered under it by an endorsement) and is normally used when financing is involved in the transactions. The customer usually needs the original (in a set of 3 originals) as proof ownership in order to take possession of the goods. A BIL, once drawn to the order of a foreign consignee would enable the foreign consignee further to endorse the B/L (i.e. to transfer the title of the goods) to another third party. A B/L is usually drawn "To the Order of the Shipper" and endorsed either "in blank" or to a "named consignee". The purpose of the endorsement is to protect the shipper's interest against the buyer's obtaining the merchandise betore the shipper has been paid or accepted the relative draft drawn from his bank. |
For more International Shipping Terms, please refer Guidebook on Export & Import Procedures in Malaysia, Malaysia Productivity Corporation.
Source: Guidebook on Export & Import Procedures in Malaysia, Malaysia Productivity Corporation
